Proper ventilation and airflow are crucial for maintaining a healthy, comfortable, and energy-efficient home. Good air circulation not only helps remove moisture and pollutants but also improves the overall quality of indoor air, keeping it fresh and breathable. When designing a home, especially from scratch or during a renovation, ensuring that you create a home with maximum ventilation and airflow should be a top priority.
In this blog, we’ll guide you through the best strategies for designing a home with maximum ventilation and airflow. From the layout and positioning of windows to the integration of modern ventilation systems, these practical tips will ensure your home stays cool in summer, warm in winter, and filled with fresh, clean air all year round.
Outline
- The importance of ventilation and airflow in home design.
- Maximizing Natural Ventilation:
- Positioning Windows for Cross-Ventilation
- Orientation of the Home
- Open Floor Plan
- Proper Window Placement and Sizing:
- Large Windows
- Operable Windows
- Strategic Placement
- Windows Screens
- Cross-Ventilation:
- Designing for Cross-Ventilation
- Airflow Pathways
- Use of Ventilation Systems:
- Exhaust Fans
- Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs)
- Whole-House Ventilation System
- Ventilation for Different Rooms:
- Kitchens
- Bathrooms
- Living Rooms and Bedrooms
- Ceiling Fans and Air Circulation:
- Fan Placement
- Additional Fans
- Building Materials that Aid Ventilation:
- Preamble Materials
- Open Space and Grid Design
- Landscaping and Outdoor Airflow:
- Strategic Planting
- Patios and Outdoor Spaces
- Conclusion: The benefits of good airflow and how to maintain it.
1. Importance of designing home with maximum ventilation and airflow
When it comes to designing a home, one aspect that often gets overlooked is the importance of ventilation and airflow. We tend to focus on aesthetics, layout, and functionality, but the way air circulates throughout a space is just as important for creating a comfortable and healthy living environment.
Without proper airflow, indoor air can become stale, humidity can build up, and pollutants can linger, creating an uncomfortable and potentially unhealthy environment. In contrast, good ventilation reduces moisture, prevents the accumulation of harmful gases, and helps maintain a fresher, healthier indoor climate.
This guide will explore various strategies to design a home with maximum ventilation and airflow, ensuring your home remains fresh, comfortable, and energy-efficient.
2. Maximizing Natural Ventilation
Natural ventilation uses outdoor air to cool and refresh indoor spaces. It’s a sustainable and energy-efficient way to improve airflow, especially when incorporated into the home’s design from the beginning.
Positioning Windows for Cross-Ventilation
To achieve effective natural ventilation, it’s crucial to position windows so that air can flow easily from one side of the home to the other. This is known as cross-ventilation, where windows placed on opposite or adjacent walls create a clear path for air to pass through. This strategy allows breezes to naturally cool the interior, reduce indoor heat buildup, and maintain a constant flow of fresh air. Including operable windows and avoiding unnecessary obstructions like large furniture or solid partitions in this airflow path enhances its effectiveness.
Orientation of the Home
In warm climates, the orientation of your home plays a vital role in promoting natural ventilation. Homes that are designed with airflow in mind can take full advantage of prevailing winds. By orienting the longest sides of the home toward the direction of the breeze, you create more surface area for wind exposure, allowing fresh air to enter easily and move through the space. Avoid blocking this natural flow with high walls, garages, or neighboring structures that can act as wind barriers.
Open Floor Plans
An open floor plan can significantly improve the circulation of air throughout the interior spaces. When key areas such as the kitchen, dining room, and living room are interconnected without full dividing walls, air can move more freely, reducing stagnant zones and promoting consistent airflow. This layout not only improves ventilation but also contributes to a brighter, more spacious feeling inside the home. Incorporating high ceilings or open stairwells can further enhance this effect by encouraging warm air to rise and escape naturally.
Natural ventilation is one of the best ways to ensure a constant flow of fresh air throughout your home. Be sure to consider the layout and placement of your home to take advantage of natural breezes and avoid blocking airflow with walls or obstacles in your pursuit of a home with maximum ventilation and airflow.
3. Proper Window Placement and Sizing
Windows are one of the most important elements of airflow in a home. The placement, size, and design of your windows can have a direct impact on how air moves through your space.
Large Windows
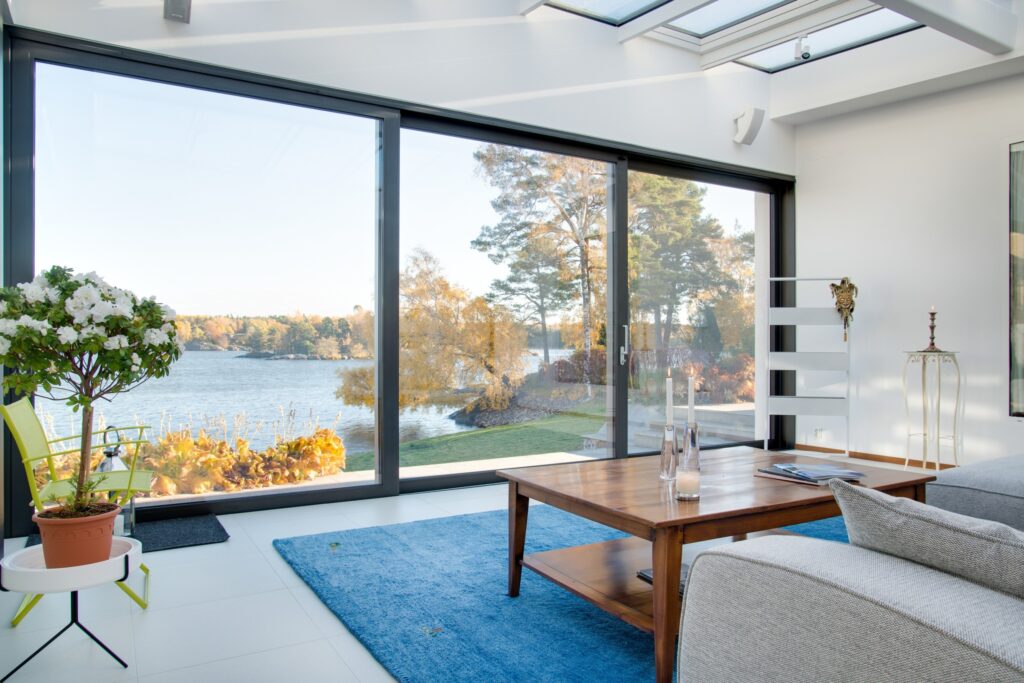

Incorporating large windows into your home’s design can greatly enhance natural ventilation. When placed on opposite walls, these larger openings support better cross-ventilation by allowing more air to enter and exit the space. The increased surface area creates stronger air currents, helping to cool the home more effectively and maintain a steady flow of fresh air throughout.
Operable Windows

Always choose windows that can be opened and closed easily to give you control over ventilation. Styles like casement or sliding windows are ideal because they can be adjusted to regulate the volume and direction of airflow based on the weather or your comfort preferences. Operable windows provide flexibility, ensuring that your space can breathe naturally year-round.
Strategic Placement
Where you place your windows is just as important as their size and functionality. Positioning windows on the windward side of the home the side facing prevailing winds maximizes the capture of outdoor breezes. High-set windows can also help by drawing warm air upward and out, while low windows bring cooler air inside, encouraging a consistent and efficient air exchange.
Window Screens
Installing quality window screens is a simple yet effective way to improve ventilation without compromising comfort. Screens allow you to keep windows open during rainy weather or in seasons when insects are prevalent, ensuring a continuous flow of fresh air without letting in pests or debris. They also add a layer of safety and privacy while maintaining the benefits of natural ventilation.
By combining large, operable windows with thoughtful placement and protective screens, you can dramatically improve your home’s natural airflow. This approach not only increases comfort but also reduces dependency on mechanical cooling systems, leading to better energy efficiency and a healthier indoor environment.
4. Cross-Ventilation
Cross-ventilation is one of the most effective ways to maintain a steady airflow in a home. This method relies on the placement of openings, like windows and doors, to create a direct flow of air from one side of the home to the other.
Designing for Cross-Ventilation
To optimize cross-ventilation, position windows on opposing walls or at varying heights across different levels of the structure. This design encourages natural air movement through the home, allowing warm air to escape and cooler air to circulate. Incorporating operable vents or clerestory windows high on walls can further assist in drawing out hot air and improving circulation.
Airflow Pathways
Ensuring that air can travel freely through the home is essential for effective ventilation. Avoid placing large furniture pieces, dense cabinetry, or heavy curtains directly in airflow paths, as these can obstruct the breeze. Keeping interior doors open especially in transitional seasons helps maintain a continuous flow of air from room to room.
Cross-ventilation is particularly important in warmer climates or areas with mild temperatures, as it reduces the need for air conditioning, making your home more energy-efficient and sustainable.
5. Use of Ventilation Systems
In addition to natural ventilation, mechanical ventilation systems can be installed to further enhance airflow and air quality. These systems are especially useful in homes where natural ventilation alone is not sufficient due to environmental factors or building design.
Exhaust Fans

Installing exhaust fans in key areas like kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry rooms is a simple yet effective way to remove excess moisture, odors, and indoor pollutants. These fans help prevent the buildup of humidity and contaminants, which can lead to mold growth or poor indoor air quality. By expelling air directly outside, they contribute to a fresher and healthier indoor environment.
Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs)
HRVs are advanced mechanical systems designed to bring in fresh outdoor air while simultaneously capturing heat from the outgoing indoor air. This exchange process minimizes energy loss, making HRVs ideal for colder climates where heating efficiency is a priority. They provide a steady flow of fresh air without causing significant temperature fluctuations, supporting both comfort and energy conservation.
Whole-House Ventilation Systems
For homes that are tightly sealed, such as modern energy-efficient buildings, a whole-house ventilation system can ensure that air circulates evenly throughout every room. These systems continuously move air, preventing stagnation and maintaining consistent indoor air quality. They are especially useful for maintaining comfort and health in a home with maximum ventilation and airflow, particularly in spaces with limited window openings or areas experiencing poor outdoor air quality.
Integrating mechanical ventilation systems can complement natural airflow, ensuring your home has constant, consistent ventilation.
6. Ventilation for Different Rooms
Different rooms in your home have unique ventilation needs. Each area requires specific attention to ensure proper airflow.
Kitchens
Kitchens generate a significant amount of heat, steam, and odors during daily cooking activities. To maintain air quality, it’s essential to install effective exhaust fans that can quickly remove these byproducts. In addition to mechanical ventilation, operable windows are a great asset allowing fresh air to flow in and steam to escape naturally. A well-ventilated kitchen not only keeps the air cleaner but also makes the space more pleasant to work in.
Bathrooms
Bathrooms are typically the most humid areas in a home, making proper ventilation crucial to prevent mold, mildew, and moisture damage. Installing a reliable ventilation fan that vents directly to the outside is essential. Where possible, include windows that can be opened to further assist with airflow and drying after showers or baths. This combination helps maintain a dry and hygienic bathroom environment.
Living Rooms and Bedrooms
For general living spaces such as living rooms and bedrooms, the focus should be on maintaining consistent, gentle air circulation without causing uncomfortable drafts. Ceiling fans are effective tools for keeping air moving and distributing cool or warm air evenly. Opening windows during cooler parts of the day such as early morning or evening can also bring in fresh air and improve overall ventilation.
By addressing the specific ventilation needs of each room, you can ensure that every area in your home remains comfortable and properly ventilated.
7. Ceiling Fans and Air Circulation
Ceiling fans are an excellent tool for improving airflow and circulation. Even in homes with great natural ventilation, ceiling fans help distribute air more evenly, preventing hot or cold spots.
Fan Placement

To get the most benefit from ceiling fans, install them in rooms that are used most frequently, such as living rooms, kitchens, and bedrooms. Proper seasonal adjustment is key: in the summer, fans should rotate counterclockwise to create a cooling breeze, while in the winter, switching to a clockwise direction helps redistribute rising warm air without causing a draft. This not only improves comfort but also helps reduce energy use for heating and cooling.
Additional Fans
In spots where ceiling fans aren’t practical such as narrow hallways, small bedrooms, or enclosed spaces portable fans like box fans or tower fans can be an effective solution. These fans help to maintain air movement in areas that may otherwise feel stagnant and can be easily relocated as needed to respond to changing airflow needs throughout the day.
Ceiling fans are an affordable and efficient way to increase airflow, especially when paired with other ventilation strategies.
8. Building Materials that Aid Ventilation
Certain building materials can help improve airflow in your home. Choosing materials that promote natural air circulation can reduce the need for mechanical systems and help maintain a pleasant indoor environment.
Permeable Materials
Materials such as brick, stone, and concrete can contribute to improved ventilation, especially when used in areas prone to moisture, like bathrooms, laundry rooms, or basements. These materials are naturally porous and allow for subtle air exchange, which can help manage humidity and prevent the buildup of damp, stale air. While they may not replace active ventilation, they work well in combination with other passive airflow strategies.
Open Spaces and Grid Design
Incorporating open or semi-open architectural elements such as open shelving, lattice partitions, and grid-style cabinetry can significantly aid in the movement of air throughout a home. These features break up solid surfaces that might otherwise block airflow and allow for passive cross-ventilation between rooms. They also add a sense of openness and visual lightness to interiors.
By selecting the right materials, you can enhance the natural ventilation of your home and reduce reliance on mechanical systems.
9. Landscaping and Outdoor Airflow
Your home’s outdoor environment can also play a role in improving indoor airflow. Landscaping can be designed to promote air circulation, allowing breezes to flow freely toward your home.
Strategic Planting
Landscaping can play a vital role in managing wind and enhancing natural ventilation around your home. Planting trees and shrubs on the leeward side (the side protected from the wind) creates a buffer that reduces the impact of strong gusts and helps stabilize indoor temperatures. On the windward side (facing the prevailing breeze), avoid dense tree coverage that could obstruct airflow. Instead, use lower, air-permeable plants or spaced-out vegetation to allow breezes to filter through and naturally ventilate your home.
Patios and Outdoor Spaces
Outdoor areas like patios, balconies, and terraces should be designed to promote free air movement. Incorporating features such as lattice panels, pergolas, or open fencing encourages airflow while still offering shade and a sense of privacy. Avoid solid barriers that block the wind completely instead, choose semi-open materials that strike a balance between shelter and ventilation. Well-designed outdoor spaces not only improve comfort but also support passive cooling strategies for adjacent indoor areas.
10. Conclusion
Designing a home with proper ventilation and airflow is more than just a matter of comfort—it’s a key element of a healthy, sustainable, and energy-efficient living environment. From the strategic placement of windows and the use of natural ventilation to the integration of mechanical systems and thoughtful landscaping, every design decision contributes to creating a home with maximum ventilation and airflow.
When airflow is optimized, indoor air stays fresh, moisture is controlled, and pollutants are reduced. This not only enhances day-to-day comfort but also supports long-term well-being and lowers energy costs by reducing reliance on artificial heating and cooling. Whether you’re building from scratch or renovating an existing space, prioritizing ventilation at every stage of design will help you create a home with maximum ventilation and airflow that feels better, functions better, and breathes better all year round.